What Is A Thermal & Ir Camera
Rut is an inevitable byproduct of work. It's generated when yous start a car's engine, go for a brisk walk or annihilation else that generates friction. Oestrus is too prevalent in electronics where it can be more difficult to manage and can exist detrimental to their continued operation. When it comes to graphics cards at that place are many ways to manage oestrus, from passive cooling, to fans and even h2o. Simply when these solutions aren't working, your GPU has one more than way to vanquish the oestrus: thermal throttling.
What is Thermal Throttling?
When your GPU takes on a heavy workload, such as gaming, it generates a load of heat. When your cooling solution can no longer dissipate heat fast enough to keep temperatures inside a rubber range, your graphics card starts to dump performance to shed heat. The core and memory frequencies brainstorm to drop---forth with your framerates---until temperatures drib to a safe operating range. All modern GPUs accept this feature in place to protect the electronic components from damage. Unmanaged, thermal throttling tin have a large touch on functioning. And, while thermal throttling itself doesn't cause any damage, the underlying crusade of throttling, rut, tin crusade damage and shorten the lifespan of your video carte.
How to Forbid Throttling
In order to maintain performance, you need to command heat, just not all graphics cards experience throttling to the same caste, or even at all. There are a multifariousness of scenarios that determine the bear on thermal throttling has on your system. Case selection, cooling solution, and airflow are the 3 principal factors to accept into consideration.
A small-scale example with no open space traps heat and inhibits airflow, which makes it harder to keep your GPU cool. Choosing a larger, well laid out case can provide more fan mounts and options to optimize airflow. Being able to mount additional fans in your case is specially beneficial if your GPU manufacturer has used a custom cooling solution that dissipates heat into your case instead of directly removing information technology, similar with reference designs.

Adding additional fans to the meridian of your case ensures that heat generated past your GPU is removed from the instance efficiently. Information technology also lowers air temperature inside of your instance keeping other components, such every bit your CPU and memory, much cooler.
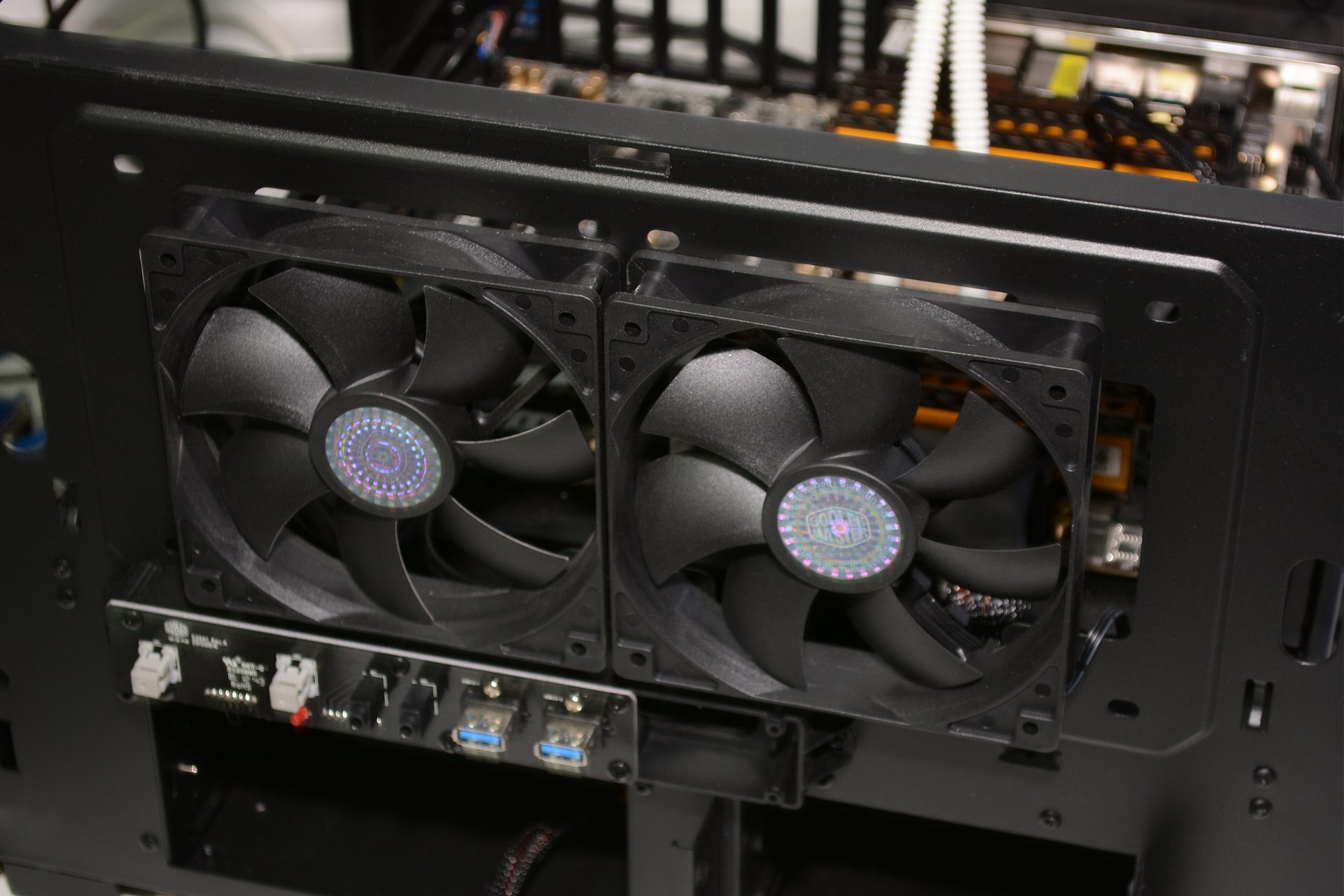

The brand of graphics carte du jour you choose may come downwardly to personal preference, but the cooling solution information technology uses is an important determination. Reference designs---which are blower-blazon fans---typically utilize a single fan to keep the card absurd. Cool air is drawn through the rear of the graphics card and exhausted out of the terminate with the connectors. This blueprint is efficient but the single fan holds back functioning.
When choosing a graphics card, information technology's frequently ideal to pick 1 with a multi-fan cooling solution. The additional fans---sometimes equally many as iii---provide plenty airflow to significantly reduce or even eliminate throttling. It should be noted that your instance needs to provide enough airflow to handle the hot air pumped out by these types of graphics cards as their coolers practice non directly remove the heat from the case.


If changing or calculation hardware is not an option, you can all the same reduce temperatures using freely available tools.
With utilities like MSI's Afterburner or EVGA's PrecisionX, a custom fan curve tin exist configured. By setting the fan curve manually, you can ready the fan speed for a given temperature to something a bit more aggressive. From the factory, the fan speeds are optimized to strike a balance betwixt noise and performance. With reference cards, this balance oftentimes leans more towards noise suppression and tin lead to thermal throttling.
Noise levels will increase, possibly significantly, only your GPU will be able dissipate rut much faster and maintain functioning.

Default Left, Custom Right
If the additional fan dissonance is too much to handle, there is one more solution to your thermal throttling woes: undervolting.
Sometimes the amount of voltage your card uses is prepare higher than it needs to be to allow your card to function correctly. Running at a college voltage generates more than rut even if the clock and memory speed remain the same. Undervolting your graphics card by even a minor amount can lower temperatures enough to reduce or even eliminate thermal throttling. However, this isn't a guaranteed solution and tin can cause stability issues. For most users, we recommend a combination of better cooling in conjunction with fan-curve adjustments.

Virtually monitoring tools are capable of more than than merely decision-making GPU fans and altering voltage. They also monitor temperatures, core and memory frequencies, along with GPU usage. Most of them besides offer at to the lowest degree basic overclocking capability. This is important because your can't prevent something that you can't see.
Monitoring your GPU's temperature, along with core and memory frequencies, allows you to make up one's mind when you're experiencing throttling. It'due south important to note that there are a few things to look for earlier yous need to break out the utilities. If you are experiencing stuttering or discover a visible drop in frame rate, information technology's likely that your video card has slowed down to shed rut. If you haven't altered your video card's fan bend and the fan is starting to sound like a jet engine, there is a skilful chance yous've hit the throttling signal. You can then confirm this with the tool of your choice.
If your temperature exceeds your graphics card'south throttling point and your frequencies start to drop, you know information technology'southward time to look at your cooling. Ideally yous want temperatures to be as depression equally possible, anything below 80 degrees is normal and should continue throttling in cheque. Nvidia's GTX 1080 Ti, for example, has a throttling point of 84 degrees. If y'all keep the temperature beneath 80 degrees you go out yourself with a bit of breathing room, then you can focus on having fun instead of monitoring GPU frequencies.
Information technology'south of import to think that every graphics card has a different throttling point. The previous-gen GTX 980 and 970, for example, throttle at 80 degrees, while AMD's Vega series cards can reach a maximum temperature of 85 degrees before they throttle. You will need to find out the throttling point for your specific carte in order to gear up an effective fan curve and voltage.
When deciding which utility to use, it'due south important to consider the scope of what y'all are going to exist monitoring. If you are going to focus on your graphics card, then I recommend MSI's Afterburning or Asus Tweak. Either of these tools will provide all the monitoring and configuration options you could possibly demand, including overclocking.
If yous want to monitor your whole organisation, you'll demand to await at something else, such equally NZXT'south Cam software. While Cam does monitor your entire system, it doesn't offer every bit many options for tweaking your graphics card. It doesn't injure to install more than than one utility to get a wider range of monitoring features.
Further Reading
- The Best CPU Coolers 2018
- How Nosotros Test: CPU Gaming Benchmarks
- The Best Graphics Cards 2018
Source: https://www.techspot.com/article/1638-what-is-thermal-throttling/
Posted by: jonesprich1962.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is A Thermal & Ir Camera"
Post a Comment